
# Android export ANDROID_SDK_ROOT =/Users/ciandroid/android-sdk-macosxĮxport PATH = $PATH: $ANDROID_SDK_ROOT/tools If you're not using bash, edit the right config file for your environment. Now it's time to set your build environment's PATH variable and other variables that will be use to locate Android.Įdit your. $ tools/bin/sdkmanager "platforms android-25" "build-tools 25.0.2" "extras google m2repository" "extras android m2repository" Run the sdkmanager tool: $ tools/bin/sdkmanager -update

The directory names can be anything you like, but save the files in somewhere easy to find (i.e. Unzip and place the contents within your home directory. Use wget with the correct SDK URL: $ wget Copy the URL for the download that's appropriate for your build machine OS. Go to Android SDK and navigate to the SDK Tools Only section. You will need to download the Android SDK without Android Studio bundled. This will install the Android SDK tools in /usr/local/Cellar/android-sdk/ Installing the Android SDK (Manual Way)
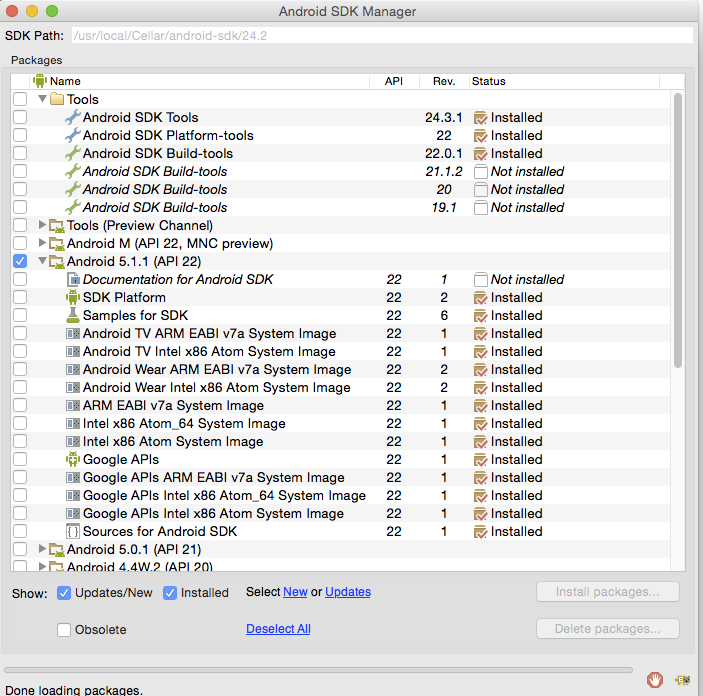
Below is an overview of all different approaches. The Android SDK can be installed automatically using the latest version of Gradle or downloading the Android SDK manually in several different ways. Platform Tools include the Android debug shell, sqlite3 and Systrace. The Build Tools primarily include aapt (Android packaging tool to create. The SDK Tools primarily includes the stock Android emulator, hierarchy viewer, SDK manager, and ProGuard.

The Android software development kit (SDK) includes different components, including SDK Tools, Build Tools, and Platform Tools.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
